Home › Health › Cancer
Cancer, Its Types, Real-time and Advanced Technology for Its Diagnosis
Published on:
Cancer has become very common in today’s world. Breast cancer in women and lung cancers in men are the most common cancers worldwide. A few years back, diagnosis for cancer was difficult.
But thanks to technological advancements and awareness nowadays, it’s not a challenge anymore.
Artificial Intelligence has proven a great help in cancer diagnosis. For example, NLP. NLP (Natural Language Processing) applications are based on neural networks. It helps oncologists extract meaningful outcomes while taking notes on patients’ treatment progress. It saves long hours of manual analysis.
Another example of AI in cancer diagnosis is the Body Vision system. It is an intraoperative CT imaging platform that enables physicians to see the actual lesion and lesion location in real-time using any C-arm, a conventional piece of X-ray equipment found in nearly every bronchoscopy procedure room. Body Vision allows pulmonologists to use real-time, intraoperative tomography to visually confirm they are taking tissue samples from exactly where' they need to be when diagnosing whether or not a patient has cancer. Body Vision’s image-guided biopsy approach provides superior clinical outcomes at a low operational cost. Its minimal footprint consists of three parts: the main unit, the tablet that provides control of the Body Vision system from any room wirelessly, and the procedural kit.
Contents
Now let us understand about cancer
Cancer is an uncontrollable growth of cells in our body. This uncontrollable growth of cells then forms a tumor. This tumor can be malignant or benign.
The malignant tumor turns into cancer. A malignant tumor means it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. But a benign tumor can grow but won’t spread anywhere' in the body.
Some types of cancer form tumors while some don’t. Breast cancers form tumors, while leukemia (blood cancer) doesn’t form tumors.
Types of Cancer
A type of cancer gets its name from its origin. There are four main types of cancers; Carcinomas, Sarcomas, Lymphomas, and Leukemias.
• Carcinomas

Cancer that begins in the skin or tissue covering the internal organs, usually forming solid tumors, are carcinomas. These are the most common types of cancer. Breast cancer, lung cancer, Prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer are carcinomas.
• Sarcomas
Cancer that begins in the tissue that connects the body in any form is a sarcoma. Sites, where' a sarcoma can develop in the body, are nerves, joints, tendons, blood vessels, cartilage, bone, fat, and muscles.
• Lymphomas
Cancer that begins in the lymphatic system is lymphomas. The network of vessels and glands that help fight infection is known as the lymphatic system. Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are the two main types of lymphomas.
• Leukemias

Cancer of blood is known as leukemia. Cancer of blood begins when the healthy blood cells change and grow uncontrollably. Acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, and chronic myeloid leukemia are four types of leukemias.
Diagnosis of Cancer
Cancer cannot be diagnosed with a single test. It is suspected based on symptoms, physical examination, and screening test results.
Multiple tests are needed to confirm it as cancer.
Different diagnosis methods for detection of cancer are:
- Lab tests
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Genetic tests
- Biopsy
- Endoscopic exams
Lab tests
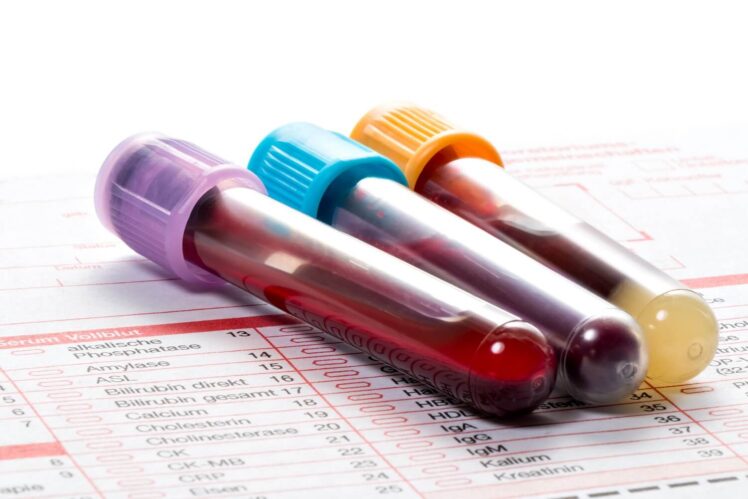
The levels of certain substances in our body can point to cancer. Blood, Urine, and other body fluids tests help doctors determine. But abnormal lab tests can not always be a sure sign of cancer. Some blood and tissue samples are taken for checking tumor markers.
Tumor markers are those substances that are either produced by the cancer cells or by other cells of the body in response to cancer. Tumor markers can not solely determine if a person has cancer because not every person with tumors has tumor markers.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic Imaging is an advanced technique where' images are used to detect abnormalities.
• CT scan

CT Scan is Computerized tomography. In a CT scan, you lie down, and a donut-shaped machine clicks pictures of your body from different angles. In a CT scan, an X-Ray machine and a computer are linked with each other. They produce a series of images. These images are then combined to form a detailed 3D image of the inside of the body. CT scan is more common and less expensive.
• MRI
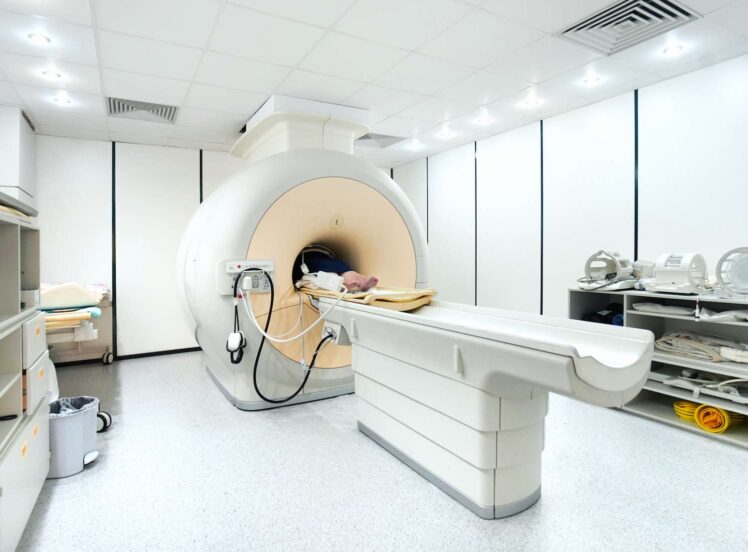
MRI is magnetic resonance imaging. MRI in radiology uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create pictures of the inside of the body. MRI produces better images.
In both CT scans and MRI, a special dye is injected into the veins to show tumors brighter to detect.
• Nuclear scan
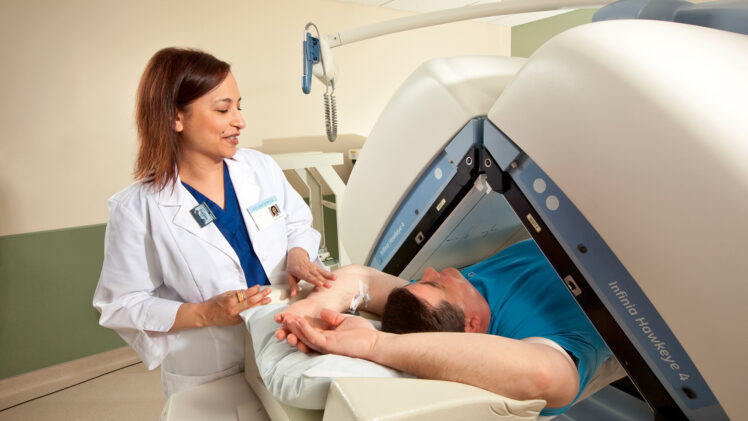
In a nuclear scan, radioactive material is released via injection into your body in small amounts, also known as a tracer. The -scanner measures the radioactivity in your body and accordingly creates pictures. The radioactive material eventually loses its radioactivity or, later it may leave your body through urine or stool. A nuclear scan is known as a radionuclide scan.
Bone scan and PET scan are also types of nuclear scan.
In a bone scan, abnormality or damage in the bones is detected.
It is also used to detect cancer that spreads through bones, known as metastatic bone tumors and bone cancers.
In this, a small amount of radioactive material is injected into the vein. This radioactive material gets collected in the abnormal areas in the bone and is visible in the scan. The areas where' the material is collected are known as “hot spots.”
Cancer cells often take up more glucose than healthy cells. A PET scan makes detailed images of the scan where' glucose is taken up, inside the body. Before the process, radioactive glucose is injected into the person.
• Ultrasound

An ultrasound uses high-energy sound waves. These sound waves echo off the tissues in the body. A computer uses this echo to create a picture known as a sonogram.
• Biopsy
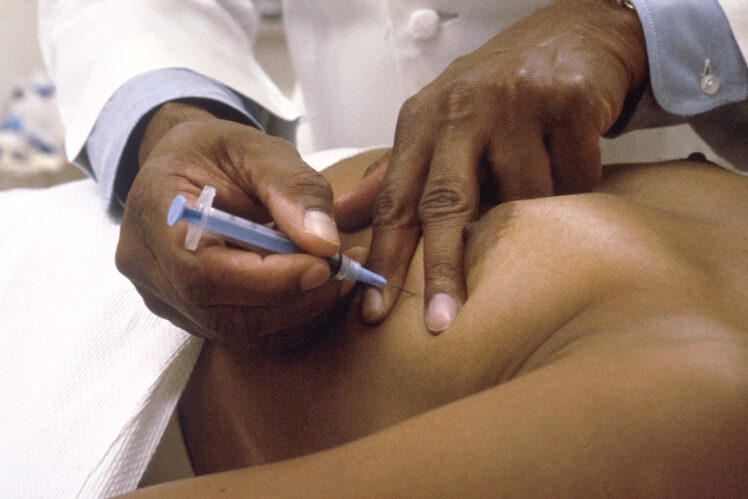
A biopsy is the most common process to diagnose cancer. In a biopsy, a doctor removes a sample tissue for further examination. Then the doctor carries out Microscopic observation tests on the sample to see if the tissue is cancerous. Samples are obtained in two ways, with a needle or with endoscopy.
With a needle, the doctor withdraws fluid or tissue. Doctors use this technique in the prostate, bone marrow aspirations, and liver biopsies.
In endoscopy, the doctor uses a thin, lighted tube known as an endoscope. An endoscope goes inside the body through natural openings like the nose, mouth, or anus.
Colonoscopy and bronchoscopy are two exams that use endoscopy.
In bronchoscopy, the endoscope goes through the nose or mouth through the throat. In bronchoscopy, the lungs, trachea, and bronchi are examined.
AI has proven to be a boon in lung cancer detection. Lungvision is one such device that applies the augmented reality approach to track bronchial nodules in real-time.
• Surgery

A biopsy is sometimes done by surgery. Surgery can be incisional biopsy or excisional biopsy. In an incisional biopsy, the surgeon removes part of the abnormal area. In an excisional biopsy, the surgeon removes the entire abnormal cells and the tissues around them.
Share With Your Friends